Amebic liver abscess
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

A collection of pus in the liver due to infection with the parasite Entamoeba histolytica.
The protozoal cyst is transmitted by the fecal-oral route. Following excystation in the intestine, the organism invades the colon. The liver is seeded by hematogenous spread.
Travel to areas with poor sanitation and high rates of amebic infection including Mexico, Central America, South America, India, and Africa is a risk factor for this infection. In the United States, immigrants from these countries may present with this condition. This infection is more common in men. Abscess formation is uncommon in children. Risk factors for severe infection due to E. histolytica include the use of corticosteroids, pregnancy, advanced age, and malnutrition.
Symptoms usually develop over 2-4 weeks, although some patients present acutely and other patients may present 2-3 months after returning from an endemic area. The hallmark symptoms are right upper quadrant abdominal pain and fever. Hepatomegaly is common, and the liver is usually tender to palpation. Children are less likely than adults to present with pain. Other symptoms may include cough, nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramping, and diarrhea.
Mortality is low unless the abscess ruptures or the abscess extends to involve adjacent structures including the pericardium.
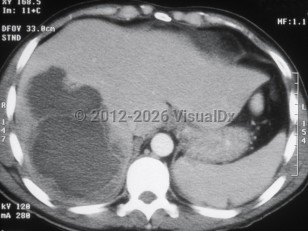
Laboratory evaluation reveals leukocytosis, elevated transaminases, and elevated alkaline phosphatase. The abscess can be visualized by computed tomography or ultrasound. Usually only one lesion is seen. Most of the time, the lesion is located in the right lobe of the liver.
Treatment includes anti-parasitic medication. Abscesses that are at high risk for rupture should be aspirated to reduce their size.
Related topic: Pyogenic Liver Abscess
The protozoal cyst is transmitted by the fecal-oral route. Following excystation in the intestine, the organism invades the colon. The liver is seeded by hematogenous spread.
Travel to areas with poor sanitation and high rates of amebic infection including Mexico, Central America, South America, India, and Africa is a risk factor for this infection. In the United States, immigrants from these countries may present with this condition. This infection is more common in men. Abscess formation is uncommon in children. Risk factors for severe infection due to E. histolytica include the use of corticosteroids, pregnancy, advanced age, and malnutrition.
Symptoms usually develop over 2-4 weeks, although some patients present acutely and other patients may present 2-3 months after returning from an endemic area. The hallmark symptoms are right upper quadrant abdominal pain and fever. Hepatomegaly is common, and the liver is usually tender to palpation. Children are less likely than adults to present with pain. Other symptoms may include cough, nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramping, and diarrhea.
Mortality is low unless the abscess ruptures or the abscess extends to involve adjacent structures including the pericardium.
Laboratory evaluation reveals leukocytosis, elevated transaminases, and elevated alkaline phosphatase. The abscess can be visualized by computed tomography or ultrasound. Usually only one lesion is seen. Most of the time, the lesion is located in the right lobe of the liver.
Treatment includes anti-parasitic medication. Abscesses that are at high risk for rupture should be aspirated to reduce their size.
Related topic: Pyogenic Liver Abscess
Codes
ICD10CM:
A06.4 – Amebic liver abscess
SNOMEDCT:
75119003 – Amebic liver abscess
A06.4 – Amebic liver abscess
SNOMEDCT:
75119003 – Amebic liver abscess
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:08/15/2016