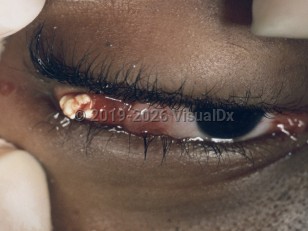
Lacrimal gland stones
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

A rare cause of chronic unilateral conjunctivitis that presents with swelling in the lateral canthal region. These stones, known as dacryoliths, are found within the lacrimal gland itself, and excision of these results in resolution of symptoms. Often asymptomatic. Common signs and symptoms include eye discharge, eyelid edema, eye pain, photophobia, and conjunctival injection. Other symptoms include intermittent itching, eye redness, and epiphora, and rarely intermittent exophthalmos. May be caused by swelling, protein, and debris in the lacrimal gland, or bacterial / fungal infection in the lacrimal gland or in lacrimal pathways.
Management is usually excision using local anesthetic, rarely with complications.
Management is usually excision using local anesthetic, rarely with complications.
Codes
ICD10CM:
H04.009 – Unspecified dacryoadenitis, unspecified lacrimal gland
SNOMEDCT:
86927009 – Dacryoadenitis
H04.009 – Unspecified dacryoadenitis, unspecified lacrimal gland
SNOMEDCT:
86927009 – Dacryoadenitis
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:02/29/2016
Lacrimal gland stones