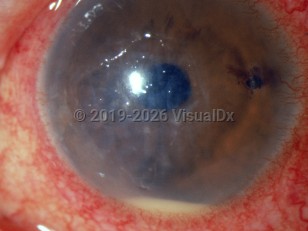
Bacterial corneal ulcer - External and Internal Eye
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Risk factors that can lead to bacterial keratitis include contact lens wear, eye trauma, previous ocular surgery, dry eye, immunosuppression, and any other process that causes breakdown of the ocular surface.
Patients with a bacterial corneal ulcer will complain of eye pain, light sensitivity, red eyes, and possibly reduced vision. The rapidity of the onset and progression of symptoms depends on the virulence of the bacteria causing the infection.
History is very important in giving clues as to the most common organism causing the infection. Bacterial keratitis in a contact lens wearer is frequently caused by gram-negative organisms, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, whereas ulcers in patients with blepharitis are more commonly due to gram-positive organisms.
Note: As of November 15, 2023, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is reminding the public not to purchase or use certain eyedrops from several major brands due to risk of eye infection. Refer to the FDA list for more information. As of January 31, 2024, the FDA is warning consumers not to purchase or use South Moon, Rebright, or FivFivGo eye drops because of the potential risk of eye infection; these are copycat products easily mistaken for Bausch + Lomb's Lumify brand eye drops.
Codes
H16.009 – Unspecified corneal ulcer, unspecified eye
SNOMEDCT:
231893002 – Bacterial corneal ulcer
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:12/03/2024