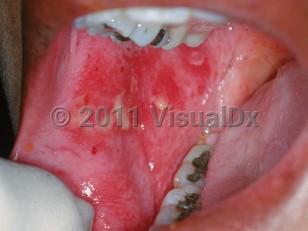
Chemotherapy-induced mucositis in Child
See also in: Oral Mucosal LesionAlerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

While not all chemotherapeutic agents will cause mucositis, many of them have this capability. Some agents (eg, methotrexate and etoposide) are excreted in saliva, which increases their toxicity. The degree to which mucositis is induced is also dependent on the drug and the age of the patient, with younger patients often experiencing more severe signs and symptoms. Chemotherapy-induced mucositis tends to be less severe in patients who have received recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF). Patients complain of pain and burning that is exacerbated by eating and by oral hygiene procedures.
Oral mucositis combined with gastrointestinal mucositis may occur in about 8% of patients who receive standard-dose chemotherapy with subsequent development of myelosuppression. Suggestive symptoms include pain, nausea / vomiting, and diarrhea.
Related topic: drug-induced oral mucositis
Codes
K12.31 – Oral mucositis (ulcerative) due to antineoplastic therapy
SNOMEDCT:
403666006 – Drug-induced mucositis
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:07/18/2024