Spina bifida in Child
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis
Neural tube defects (NTDs) arise from abnormalities in the formation of the structures along the craniospinal axis that occur due to a complex interaction of genetic and environmental factors. Risk factors for NTDs include women with a previous NTD-affected pregnancy, maternal pregestational diabetes, hyperthermia, specific anticonvulsant drugs such as valproic acid, and folic acid deficiency; a potential association between dolutegravir (an antiretroviral) exposure at conception and the development of NTDs has been reported.
Although the underlying pathophysiology is not completely understood, folic acid plays an important role in the prevention of NTDs such as spina bifida. Taking folic acid supplementation during childbearing years and mandating the fortification of food with folic acid has significantly reduced the risk of having an NTD-affected pregnancy. Marked increases of spina bifida and myelomeningocele have been seen in Ethiopia due to lack of folic acid.
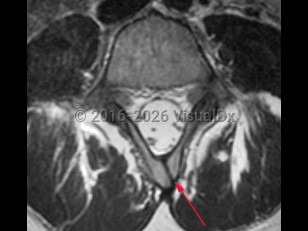
NTDs are classified as open (neural tissue exposed; anencephaly, myelomeningocele, meningocele) or closed (skin covering the defect; spina bifida occulta). Spina bifida occulta, also known as closed spinal dysraphism, is the least severe of the NTDs and results from the incomplete fusion of the posterior vertebral bodies, typically in the lumbosacral spine. Here we will focus on spina bifida occulta.
Spina bifida occulta may be suspected due to the presence of cutaneous lesions such as a dermal sinus tract, sacral dimple, hypertrichosis, hemangiomas, or a subcutaneous lipoma. Cases of spina bifida occulta can present at any age, and the severity of symptoms varies from asymptomatic to severe neurologic impairment due to tethered cord syndrome, secondary to abnormal tension on the spinal cord. Signs and symptoms of tethered cord syndrome secondary to spina bifida occulta include gait changes, bowel / bladder dysfunction, leg and back pain, and orthopedic deformities.
Although the underlying pathophysiology is not completely understood, folic acid plays an important role in the prevention of NTDs such as spina bifida. Taking folic acid supplementation during childbearing years and mandating the fortification of food with folic acid has significantly reduced the risk of having an NTD-affected pregnancy. Marked increases of spina bifida and myelomeningocele have been seen in Ethiopia due to lack of folic acid.
NTDs are classified as open (neural tissue exposed; anencephaly, myelomeningocele, meningocele) or closed (skin covering the defect; spina bifida occulta). Spina bifida occulta, also known as closed spinal dysraphism, is the least severe of the NTDs and results from the incomplete fusion of the posterior vertebral bodies, typically in the lumbosacral spine. Here we will focus on spina bifida occulta.
Spina bifida occulta may be suspected due to the presence of cutaneous lesions such as a dermal sinus tract, sacral dimple, hypertrichosis, hemangiomas, or a subcutaneous lipoma. Cases of spina bifida occulta can present at any age, and the severity of symptoms varies from asymptomatic to severe neurologic impairment due to tethered cord syndrome, secondary to abnormal tension on the spinal cord. Signs and symptoms of tethered cord syndrome secondary to spina bifida occulta include gait changes, bowel / bladder dysfunction, leg and back pain, and orthopedic deformities.
Codes
ICD10CM:
Q05.9 – Spina bifida, unspecified
SNOMEDCT:
67531005 – Spina bifida
Q05.9 – Spina bifida, unspecified
SNOMEDCT:
67531005 – Spina bifida
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Reviewed:06/19/2019
Last Updated:12/17/2019
Last Updated:12/17/2019
Spina bifida in Child