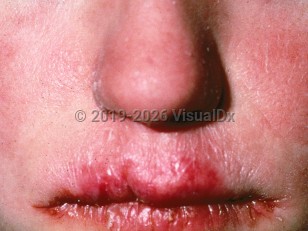
Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis in Adult
See also in: Nail and Distal DigitAlerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Persistent Candida infection of the mouth, skin, and nails that is refractory to conventional topical therapy occurs as a distinct syndrome called chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis (CMC). Patients with CMC have an ineffective immune response to Candida species, most commonly Candida albicans. The immunodeficiencies that predispose to Candida infections involve impaired T helper 17 (Th17) cell function.
In some cases, susceptibility to candidal infection is an isolated immunodeficiency (CMC disease). In these cases, there is a genetic defect in the IL17F or IL17RC genes. The most common mutation causing CMC is a STAT1 gain of function mutation. Patients with STAT1 mutations may also have autoimmune diseases such as thyroid disease, alopecia areata, or type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Mutations in the AIRE gene cause autoimmune polyendocrinopathy, candidiasis, and ectodermal dysplasia (APECED), in which CMC is the major infectious feature. Individuals with hyper-IgE syndrome also may have CMC.
Most cases of CMC are seen in childhood and adolescence. A family history may or may not be present. Patients with an associated endocrinopathy will have systemic symptoms and signs in addition to mucocutaneous manifestations. Many patients have concomitant dermatophyte infection. Most do not develop disseminated Candida infection. Many patients also develop infections other than those caused by Candida such as staphylococcal infections, bacterial pneumonia, and viral infections. Susceptibility to non-candidal infections depends on the specific variant of CMC.
Severity of disease is highly variable, with some patients improving with age (particularly in the autosomal recessive disease), while other patients may not survive. The course is chronic.
In some cases, susceptibility to candidal infection is an isolated immunodeficiency (CMC disease). In these cases, there is a genetic defect in the IL17F or IL17RC genes. The most common mutation causing CMC is a STAT1 gain of function mutation. Patients with STAT1 mutations may also have autoimmune diseases such as thyroid disease, alopecia areata, or type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Mutations in the AIRE gene cause autoimmune polyendocrinopathy, candidiasis, and ectodermal dysplasia (APECED), in which CMC is the major infectious feature. Individuals with hyper-IgE syndrome also may have CMC.
Most cases of CMC are seen in childhood and adolescence. A family history may or may not be present. Patients with an associated endocrinopathy will have systemic symptoms and signs in addition to mucocutaneous manifestations. Many patients have concomitant dermatophyte infection. Most do not develop disseminated Candida infection. Many patients also develop infections other than those caused by Candida such as staphylococcal infections, bacterial pneumonia, and viral infections. Susceptibility to non-candidal infections depends on the specific variant of CMC.
Severity of disease is highly variable, with some patients improving with age (particularly in the autosomal recessive disease), while other patients may not survive. The course is chronic.
Codes
ICD10CM:
B37.2 – Candidiasis of skin and nail
SNOMEDCT:
234568006 – Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis
B37.2 – Candidiasis of skin and nail
SNOMEDCT:
234568006 – Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Reviewed:01/25/2021
Last Updated:01/12/2022
Last Updated:01/12/2022
Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis in Adult
See also in: Nail and Distal Digit