Telogen effluvium in Child
See also in: Hair and ScalpAlerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Drugs implicated include acitretin, isotretinoin, high-dose vitamin A, beta blockers (metoprolol, nadolol, propranolol, and topical timolol), bromocriptine, captopril, cimetidine, antidepressants (fluoxetine), sulfasalazine, anticonvulsants (eg, valproic acid and lamotrigine), interferons, antihyperlipidemic drugs, diabetic drugs, androgens, oral contraceptives, anticoagulants (warfarin, heparin), albendazole, and chemotherapeutic agents. Drug-induced hair loss is usually reversible after cessation of medication use. Cases have been identified after viral infections, such as human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination in children, human immunodeficiency virus infection, and dengue fever in adults.
The interval between the inciting event or exposure and the shedding is generally weeks to a few months. In adults, the cause is often never identified. In children, etiology may be easier to discern. Telogen effluvium may occur as a normal physiological phenomenon in this age group.
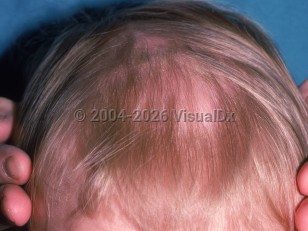
Telogen effluvium primarily affects women in the fourth to seventh decade of life. Patients present complaining of a sudden increase in hair shedding from the root with a small white hair bulb, often after showering or during combing. The hair loss occurs uniformly over the entire scalp and is usually asymptomatic, without stinging or pruritus. Hair loss usually exceeds 150 hairs daily and may continue for 6-12 months. Less commonly, a chronic form of telogen effluvium can last several years. While it may occur after common triggers of telogen effluvium, it may begin without a clear etiology.
Telogen effluvium itself is a benign and self-limited condition, although its presence may provide a clue to an underlying disease.
Related topics: Drug-induced alopecia, Anagen effluvium
Codes
L65.0 – Telogen effluvium
SNOMEDCT:
39479004 – Telogen effluvium
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:10/11/2022
 Patient Information for Telogen effluvium in Child
Patient Information for Telogen effluvium in Child- Improve treatment compliance
- Reduce after-hours questions
- Increase patient engagement and satisfaction
- Written in clear, easy-to-understand language. No confusing jargon.
- Available in English and Spanish
- Print out or email directly to your patient