Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome in Infant/Neonate
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

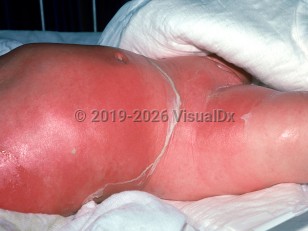
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (SSSS), or Ritter disease, is an acute disease caused by epidermolytic toxins released by strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Newborns are particularly susceptible to these exfoliative toxins. Oftentimes, focal infection of the nasopharynx, conjunctivae, perineum, or umbilicus produces toxins that lead to diffuse fragile bullae, which are often no longer intact at the time of presentation. However, any systemic or cutaneous infection with epidermolytic toxin-producing S. aureus may induce SSSS. Infants are believed to have increased susceptibility to SSSS due to lack of neutralizing antibodies and decreased renal capacity for toxin excretion.
In the newborn, presentation generally occurs between 3-7 days of life, with only one reported case of congenital SSSS. Symptoms occur acutely, with sudden onset of fever, irritability, cutaneous tenderness, and characteristic cutaneous eruption. Symptoms of SSSS can occur in conjunction with bullous impetigo. Full recovery occurs in most cases. Sepsis (with multisystemic involvement) and fluid and electrolyte abnormalities are possible.
In the newborn, presentation generally occurs between 3-7 days of life, with only one reported case of congenital SSSS. Symptoms occur acutely, with sudden onset of fever, irritability, cutaneous tenderness, and characteristic cutaneous eruption. Symptoms of SSSS can occur in conjunction with bullous impetigo. Full recovery occurs in most cases. Sepsis (with multisystemic involvement) and fluid and electrolyte abnormalities are possible.
Codes
ICD10CM:
L00 – Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
SNOMEDCT:
200946001 – Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
L00 – Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
SNOMEDCT:
200946001 – Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Reviewed:06/08/2017
Last Updated:06/14/2017
Last Updated:06/14/2017
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome in Infant/Neonate