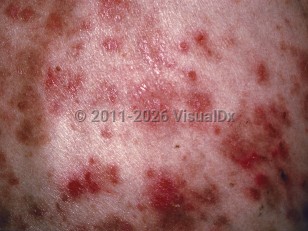
Pemphigus foliaceus in Adult
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

PF is generally considered a more benign form of pemphigus, and most patients do not become severely ill. However, in rare cases, lesions can progress to exfoliative erythroderma, potentially causing metabolic derangements. Oral lesions are rare (mucous membranes are more commonly affected in pemphigus vulgaris). Skin lesions can persist for years.
PF may be seen in any age group but tends to be a disease of adults. An exception is the endemic subtype of PF (fogo selvagem) that can affect children and young adults in endemic areas (ie, Brazil, other parts of Latin America, and Tunisia). Pathogenesis of endemic PF is complex, involving genetic, environmental, and immunological factors. Environmental factors include the bite of some insects, such as the Similium black fly (Simulium nigrimanum). Pemphigus erythematosus (Senear-Usher syndrome) is another PF subtype and is considered a less severe form of the disease that typically affects the malar region and, rarely, also affects the seborrheic areas. Pemphigus erythematosus may coexist with other autoimmune disorders, such as myasthenia gravis or lupus erythematosus. It has also been reported in association with medications such as penicillamine. See Drug Reaction Data for more information.
Sun exposure or ionizing radiation are known triggers for PF.
Codes
L10.2 – Pemphigus foliaceous
SNOMEDCT:
35154004 – Pemphigus foliaceus
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:04/24/2025