Lipoblastoma in Child
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

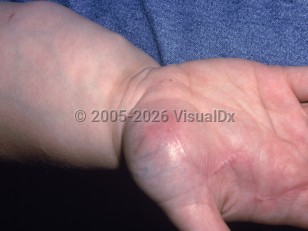
Lipoblastoma is a term used to describe encapsulated, soft subcutaneous neoplasms of immature fat, while lipoblastomatosis is a term used to describe unencapsulated and more infiltrating lesions. They are tumors of infancy primarily affecting neonates and infants. Males are affected twice as often as females. The most common locations are the extremities, trunk, and face. Parents usually notice a soft, subcutaneous or deep, mobile, soft tissue mass that can range in size from 1-12 cm on the extremity of a neonate or infant. Lipoblastomas are easily treated by complete excision and rarely recur because they are encapsulated, but lipoblastomatosis has a higher incidence of recurrence given its diffuse nature.
Codes
ICD10CM:
D17.9 – Benign lipomatous neoplasm, unspecified
SNOMEDCT:
400102008 – Lipoblastoma
D17.9 – Benign lipomatous neoplasm, unspecified
SNOMEDCT:
400102008 – Lipoblastoma
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:12/16/2021
Lipoblastoma in Child