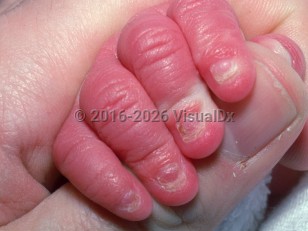
- Ankyloblepharon-ectodermal dysplasia-cleft lip / palate (AEC) syndrome
- Ectrodactyly-ectodermal dysplasia-cleft lip / palate (EEC) syndrome
- Acro-dermato-ungual-lacrimal-tooth (ADULT) syndrome
- Limb-mammary syndrome
- Split-hand / foot malformation type 4 (SHFM4)
- Isolated cleft lip / cleft palate (orofacial cleft 8 [OFC8] syndrome)
All ectodermal dysplasias result from the abnormal development of structures derived from the outer embryonal layer such as the skin, hair, teeth, nails, and eccrine and sebaceous glands. While these 6 syndromes are classified as distinct entities, their overlapping phenotypes suggest that they may be part of a spectrum of related syndromes.
p63 is a transcription factor with homology to the tumor suppressor p53. Studies in mice have demonstrated that, unlike p53, p63 expression is localized to whiskers, oral mucosa, and distal limbs. Furthermore, mice lacking p63 are born with translucent skin and without appendages (whisker pads, teeth). It has been postulated that p63 plays an important role in epidermal stratification and the maintenance of epidermal stem cells.
While all 6 syndromes show abnormalities in p63, each syndrome tends to demonstrate mutations in specific domains. EEC, OFC8, SHFM4, and ADULT syndrome are associated with missense mutations in the DNA binding domain. In contrast, mutations in the sterile alpha motif / transcription inhibitory domain (SAM/TID), which is downstream of the DNA binding domain, result in AEC syndrome phenotypes. Missense mutations in between the transactivation domain and DNA binding domain or truncation of the SAM/TID are typical of limb-mammary syndrome.