Acne fulminans in Child
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

While the pathogenesis of acne fulminans remains to be fully elucidated, the main inciting antigen is believed to be from Cutibacterium acnes (formerly known as Propionibacterium acnes). Testosterone exacerbates the process by increasing sebum excretion and the population density of C acnes.
Risk factors for acne fulminans include chronic severe acne (mean duration of 2 years), isotretinoin use (usually in high doses), a positive family history, high testosterone levels, and history of anabolic steroid use.
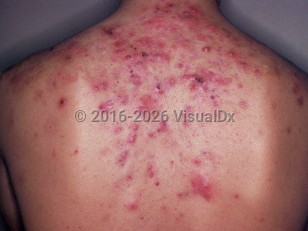
In acne fulminans without systemic symptoms (AF-WOSS), patients present with a sudden onset of large inflammatory cysts, nodules, papules, pustules, and abscesses. In acne fulminans with systemic symptoms (AF-SS), patients are febrile with systemic complaints, which may include polyarthralgia, myalgias, malaise, anorexia, and weight loss. Splenic tenderness, erythema nodosum, and bone pain from aseptic osteolysis have been reported.
When isotretinoin treatment induces acne fulminans in individuals with severe acne, this is known as isotretinoin-induced acne fulminans without systemic symptoms (IIAF-WOSS) since systemic symptoms are typically absent. In rare cases, systemic symptoms accompany, and the diagnosis is known as isotretinoin-induced acne fulminans with systemic symptoms (IIAF-SS).
Acne fulminans can be the dermatologic manifestation of SAPHO (synovitis, pustulosis, hyperostosis, and osteitis), PAPA (pyogenic arthritis, pyoderma gangrenosum, and acne), PASH (pyoderma gangrenosum, acne, and suppurative hidradenitis), and PAPASH (pyogenic arthritis, pyoderma gangrenosum, acne, and suppurative hidradenitis) syndromes.
Codes
L70.8 – Other acne
SNOMEDCT:
4659007 – Acne fulminans
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:09/12/2021