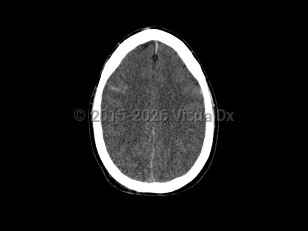
Cerebral edema
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

Cerebral edema is characterized by blurred vision, intracranial hypertension, headache, and loss of consciousness. Other common signs and symptoms are nausea, vomiting, sudden elevated blood pressure, mental status alteration, and decreased heart rate. It presents a life-threatening medical emergency leading to herniation, coma, and brain death.
Causes include severe brain trauma, ischemic stroke, meningitis, encephalitis, hepatic encephalopathy, brain cancer, diabetic ketoacidosis, eclampsia, or cerebral infarction. It also occurs as a form of high-altitude edema. Cerebral edema may occur in infants and adults.
Management aims to reduce intracranial pressure and excess brain fluid and includes corticosteroids, osmotic agents, diuretics, inotropics and other pharmacotherapy, decompression, and surgery.
Codes
G93.6 – Cerebral edema
SNOMEDCT:
2032001 – Cerebral Edema
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
Drug Reaction Data
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:04/05/2018